Hemorrhoidectomy
Introduction
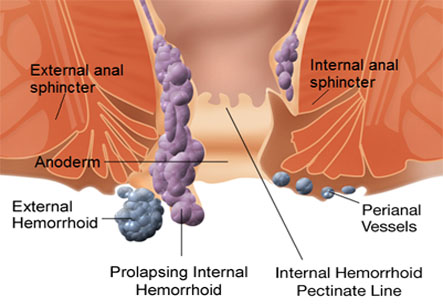
Hemorrhoids or piles are enlarged or dilated veins that are located in and around the rectum and anus. There are two types of hemorrhoids: external and internal. External hemorrhoids are those which occur below the anal sphincter and protrude at the anal opening. Internal hemorrhoids form above the anal sphincter and they do not cause much pain as there are very few pain sensing nerves in this part.
Hemorrhoids are dilated blood vessels of the anal canal. The hemorrhoidal veins are located in the lowest area of the rectum and the anus. The walls of dilated veins become stretched and are irritated by passing bowel movements.
Bleeding is the most common presenting symptom of hemorrhoidal disease
Hemorrhoidectomy is surgery to remove hemorrhoids. The procedure is as follows:
1. Hemorrhoidectomy is done as a day care procedure or may require an overnight stay in the hospital.
2. This surgery is done under general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia with sedation so that no pain is felt during the procedure.
3. Surgical incision is taken in the tissue around the hemorrhoidal vein. The swollen and dilated vein is tied off using sutures to prevent bleeding and the hemorrhoid is removed.
4. This procedure is repeated with other hemorrhoidal veins. The surgical area can be closed by sutures or left open. Medicated dressings are given.
5. This surgery can also be done by an electric instrument called cautery pencil. It cauterizes or burns the vein to seal it off.
Hemorrhoidopexy:
This surgery is done under general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia with sedation so that no pain is felt during the procedure.
In this procedure, a circular stapling device is used to remove the hemorrhoidal tissue and close the wound. Incision is not required. The hemorrhoidal vein is just lifted and then stapled back again into place in the anal canal. This surgery is also called as stapled hemorrhoidopexy. This surgery cause less pain than the conventional hemorrhoid surgery. But the drawbacks of this stapled surgery are it is more expensive and there is more possibility of recurrence of hemorrhoids.
After the surgery:
1. Immediately after the surgery, a long acting anesthetic is given for prolonged pain relief for about 6 to 12 hours.
2. Patient is taken to hospital room and monitored till the effect of anesthesia wears off.
3. First urination is very important after surgery as edema of tissues or reactive spasm of pelvic floor muscles can lead to retention of urine.
4. Patient can generally go home 1 day after the surgery.
Care after surgery:
1. Recovery after surgery takes about 2 to 3 weeks.
2. Some pain is normal after surgery. It can be controlled by usual pain relievers.
3. Bleeding can occur during first few bowel movements.
4. More liquids and a bland diet like bananas, dry toasts and plain rice should be taken for a few days. Gradual return to regular diet is recommended. Foods containing fibers is good while recovering.
5. Numbing jellies or ointments need to be used before and after bowel movements to relieve pain.
6. A course of antibiotics such as metronidazole is advised to prevent infection by some surgeons.
7. Ice packs should be applied to control swelling and pain.
8. A special bath known as sitz bath which includes soaking in medicated warm water is useful to relieve muscle spasm and pain.
9. Stool softeners containing fiber can make the bowel movements more smooth and effortless. These are used to prevent straining which can cause recurrence of piles.
10. Follow up examination can be scheduled with the surgeon after 2 to 3 weeks of surgery.
Indications:
Hemorrhoidectomy is done for:
1. Internal hemorrhoids which do not respond to conservative management.
2. Large internal hemorrhoids.
3. Large external piles causing severe discomfort.
4. Both internal and external hemorrhoids.
5. After failure of band ligation.
Results:
Surgery usually cures the hemorrhoids. But the long-term success of hemorrhoid surgery depends on changing the bowel habits and to avoid constipation and straining during defecation. Repeat surgery is needed in a few patients.
Risks:
Common complications:
Pain, bleeding, and retention of urine are common problems after hemorrhoidectomy.
Uncommon complications are divided in two groups:
a) Early complications:
1. Bleeding
2. Collection of blood in the area of surgery or hematoma
3. Bladder or bowel incontinence
4. Infection
5. Fecal impaction in anal canal
b) Late complications:
1. Anal canal narrowing.
2. Recurrence
3. Formation of abnormal passage between anal canal and any another site
4. Prolapse of rectum which is rare.